My Store
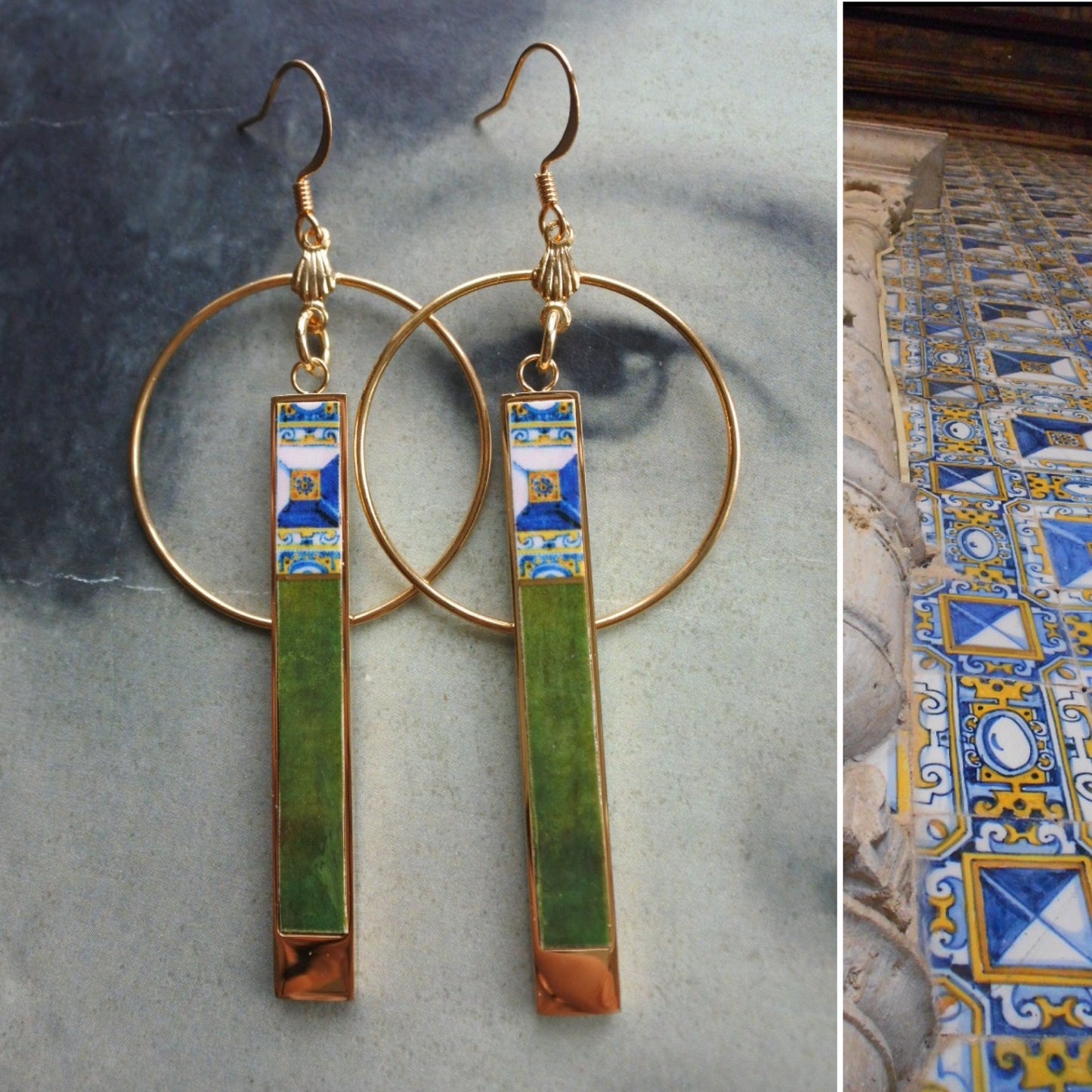
Atrio Earrings Tile Portugal Matchstick Circle Bar Azulejo 17th Century Tomar Santa Iria Church Diamond Point Tiles Emerald Green 2 options
Atrio Earrings Tile Portugal Matchstick Circle Bar Azulejo 17th Century Tomar Santa Iria Church Diamond Point Tiles Emerald Green 2 options
Couldn't load pickup availability
Use this link to find all of our Circle Bar Earrings https://www.etsy.com/shop/Atrio?section_id=29230698
WEAR A PIECE OF HISTORY!
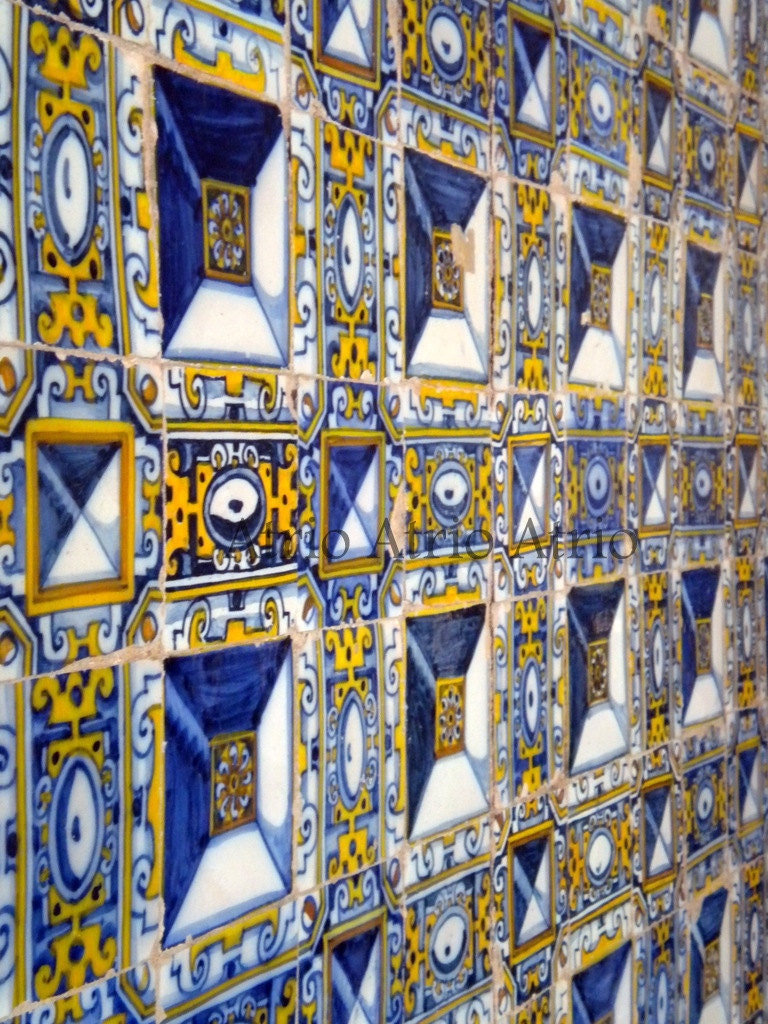
The Santa Iria Church was built in the 16th century and stands next to the Convent of Santa Iria, which is now abandoned. The entire church is covered from floor to ceiling with tiles! The tiles in this church are called "Diamond point" because the center looked like a pyramid or diamond. They are made up of a set of 9 tiles. The tiles in this church are the oldest Diamond Point tiles in Portugal. 1602 - They can also be found in a royal palace in Spain. The original maker of these was from North Africa in the 16th century.
The earrings are 3.20" long and lightweight - 4gr. each. They have stainless steel pendants and surgical steel ear wire. The silver version has a 925 silver ear wire. Vintage brass hoops. They will come in a gift box and they are reversible.
According to Wikipedia:
The castle of Tomar was built around 1160 on a strategic location, over a hill and near river Nabão. It has an outer defensive wall and a citadel (alcáçova) with a keep inside. The Keep, a central tower of residential and defensive functions, was introduced in Portugal by the Templars, and the one in Tomar is one of the oldest in the country. Another novelty introduced in Portugal by the Templars( learned from decades of experience in Normandy and Brittany and elsewhere) are the round towers in the outer walls, which are more resistant to attacks than square towers. When the town was founded, most of its residents lived in dwellings located inside the protective outer walls of the castle.
The Romanesque round church is a Roman Catholic Church from the castle (charola, rotunda) was built in the second half of the 12th century by the Knights Templar. From the outside, the church is a 16-side polygonal structure, with strong buttresses, round windows and a bell-tower. Inside, the round church has a central, octagonal structure, connected by arches to a surrounding gallery (ambulatory). The general shape of the church is modelled after similar round structures in Jerusalem: the Mosque of Omar and the Church of the Holy Sepulchre.
The capitals of the columns are still Romanesque (end of 12th century) and depict vegetal and animal motifs, as well as a Daniel in the Lions' Den scene. The style of the capitals shows the influence of artists working on the Cathedral of Coimbra, which was being built at the same time as the round church.
The interior of the round church is magnificently decorated with late gothic/manueline sculpture and paintings, added during a renovation sponsored by King Manuel I starting in 1499. The pillars of the central octagon and the walls of the ambulatory have polychrome statues of saints and angels under exuberant Gothic canopies, while the walls and ceilings of the ambulatory are painted with Gothic patterns and panels depicting the life of Christ. The paintings are attributed to the workshop of the court painter of Manuel I, the Portuguese Jorge Afonso, while the sculptured decoration is attributed to Flemish sculptor Olivier de Gand and the Spaniard Hernán Muñoz. A magnificent panel depicting the martyrdom of Saint Sebastian, by Portuguese painter Gregório Lopes, was painted for the Round Church and now hangs in the National Museum of Ancient Art in Lisbon.
During the administration of Prince Henry the Navigator (first half of the 15th century), a gothic nave was added to the round church of the Convent, thus turning the round church into a church apse. From 1510 onwards, King Manuel I ordered the rebuilding of the nave in the style of the time, a mix of late gothic and renaissance that would be called Manueline style by art historians. The architects involved were the Portuguese Diogo de Arruda and the Spaniard João de Castilho.
From the outside, the rectangular nave is covered by abundant Manueline motifs, including gargoyles, gothic pinnacles, statues and "ropes" that remind the ones used in the ships during the Age of Discovery, as well as the Cross of the Order of Christ and the emblem of King Manuel I, the armillary sphere. The so-called Window of the Chapter House (Janela do Capítulo), a huge window visible from the Saint Barbara Cloister in the Western façade of the nave, carries most of the typical Manueline motifs: the symbols of the Order of Christ and of Manuel I, and fantastic and unprecedented elaborations of ropes, corals and vegetal motifs. A human figure in the bottom of the window probably represents the designer, Diogo de Arruda. This window of the Convent constitutes one of the masterworks of Manueline decoration. Above is a smaller circular window and a balustrade. The façade is divided by two string courses of knotted ropes. The round angle buttresses are decorated with gigantic garters (alluding to investiture of Manuel I by the Order of the Garter by the English king Henry VII).
The entrance of the church is done through a magnificent lateral portal, also decorated with abundant Manueline motifs and statues of the Virgin with the Child as well as the Prophets of the Old Testament. This portal was designed by João de Castilho around 1530.
In the interior, the Manueline nave is connected to the Romanesque round church by a large arch. The nave is covered by beautiful ribbed vaulting and has a high choir that used to have Manueline choir stalls, unfortunately destroyed by invading Napoleonic troops in the early 19th century. Under the high choir there is a room that used to be the sacristy of the church. Its window is the famous Chapter House Window already mentioned.
The Convent of Christ has a total of eight cloisters, built in the 15th and 16th centuries. Some examples:
Claustro da Lavagem (Washing Cloister): Two-storey gothic cloister built around 1433 under Henry the Navigator. The garments of the monks used to be washed in this cloister, hence the name.
Claustro do Cemitério (Cloister of the Cemetery): Also built under Henry the Navigator, this gothic cloister was the burial site for the knights and monks of the Order. The elegant twin columns of the arches have beautiful capitals with vegetal motifs, and the walls of the ambulatory are decorated with 16th-century tiles. In a manueline tomb (circa 1523) rests Diogo da Gama, brother of navigator Vasco da Gama.
Claustro de Santa Bárbara (Saint Barbara's Cloister): Built in the 16th century. The Chapter House Window and the West façade of the manueline nave of the church are visible from this cloister.
Claustro de D. João III (Cloister of John III): Started under King John III of Portugal, was finished during the reign of Philip I of Portugal (also King of Spain under the name of Philip II). The first architect was the Spaniard Diogo de Torralva, who began the work in 1557, to be finished in 1591 by Philip II's architect, the Italian Filippo Terzi. This magnificent, two-storey cloister connects the dormitory of the monks to the church, and is considered one of the most important examples of Mannerist architecture in Portugal. The storeys are connected to each other by four elegant helicoidal stairways, located at each corner of the cloisters.
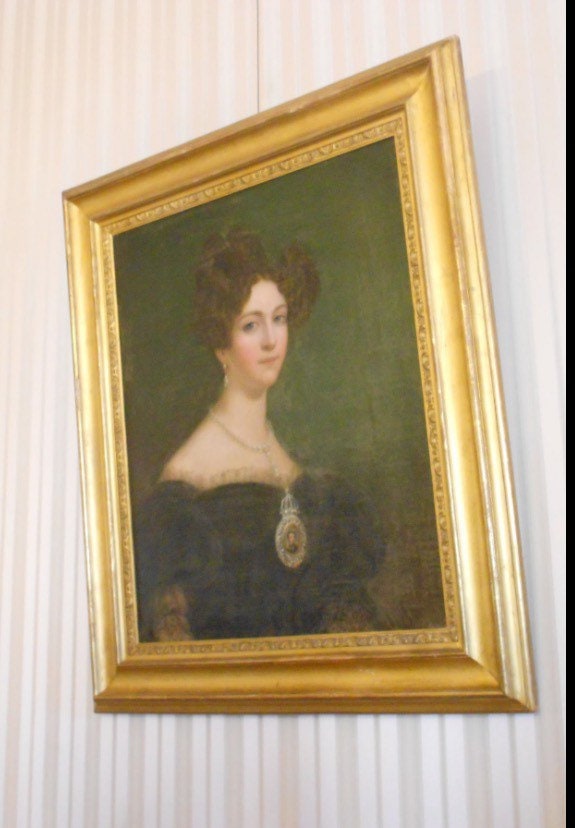
The Emerald Green bottom is from a 19th century portrait of
(According to Wikipedia)
Amélie of Leuchtenberg (Portuguese: Amélia Augusta Eugénia Napoleona de Leuchtenberg; French: Amélie Auguste Eugénie Napoléonne de Leuchtenberg), (31 July 1812 – 26 January 1873) was Empress of Brazil as the wife of Pedro I of Brazil.
She was the granddaughter of Josephine de Beauharnais, Empress of the French. Her father, Eugène de Beauharnais, was the only son of Empress Josephine and her first husband Alexandre, Viscount of Beauharnais. He thus became a stepson of Napoleon Bonaparte when his mother married the future emperor. The mother of Empress Amélie was Princess Augusta, daughter of Maximilian I, King of Bavaria.
The portrait is located in The Palace of Queluz (Portuguese: Palácio de Queluz, Portuguese pronunciation: [kɛˈɫuʃ]) is a Portuguese 18th-century palace located at Queluz, a freguesia of the modern-day Sintra Municipality, in the Lisbon District. One of the last great Rococo buildings to be designed in Europe,[1] the palace was conceived as a summer retreat for Dom Pedro of Braganza, later to become husband and then king consort to his own niece, Queen Maria I. It served as a discreet place of incarceration for Queen Maria as her descent into madness continued in the years following Dom Pedro's death in 1786. Following the destruction by fire of the Ajuda Palace in 1794, Queluz Palace became the official residence of the Portuguese prince regent, John VI, and his family and remained so until the Royal Family fled to the Portuguese colony of Brazil in 1807 following the French invasion of Portugal.[2]
Work on the palace began in 1747 under the architect Mateus Vicente de Oliveira. Despite being far smaller, the palace is often referred to as the Portuguese Versailles.[3] From 1826, the palace slowly fell from favour with the Portuguese sovereigns. In 1908, it became the property of the state. Following a serious fire in 1934, which gutted one-third of the interior, the palace was extensively restored, and today is open to the public as a major tourist attraction.
One wing of the palace, the Pavilion of Dona Maria, built between 1785 and 1792 by the architect Manuel Caetano de Sousa, is now a guest house allocated to foreign heads of state visiting Portugal.
Queluz's architecture is representative of the final extravagant period of Portuguese culture that followed the discovery of Brazilian gold in 1690.[4] From the beginning of the 18th century many foreign artists and architects were employed in Portugal to satisfy the needs of the newly enriched aristocracy; they brought with them classical ideas of architecture which derived from the Renaissance. In its design, Queluz is a revolt against the earlier, heavier, Italian-influenced Baroque which preceded the Rococo style throughout Europe.[4]
Comparisons with the far larger and more Baroque Versailles are unwarranted: Versailles is referred to as having "an aura of majesty" and it was built and dedicated to exhibit in stone "all the glories of France,"[5] whereas the far smaller palace at Queluz has been described as "exquisite rather than magnificent" and looking like "a very expensive birthday cake".[6] In its frivolity, the architecture of Queluz reflects the lifestyle led by the Portuguese royal family at the time of building: during the reign of Dom Pedro's brother, Joseph I, when Portugal was in practice governed by a valido or favourite, the Marquis of Pombal. Pombal encouraged the royal family to while away their days in the country and leave affairs of state to him.[4] Thus the extravagant, almost whimsical architecture of Queluz, set apart from the capital city, exactly represents the politics and social events of Portugal during this era, and the carefree and flamboyant lives led by its occupants.[4] Queluz's role as a haven for those without responsibility was, however, to be short-lived.
On the accession to the throne of Dom Pedro's wife Maria in 1777, Pombal was dismissed, and Dom Pedro and Maria ruled jointly in his place, using the partially completed Rococo palace at Queluz as a retreat from affairs of state in much the same way as Frederick the Great used Europe's other famed Rococo palace, Sanssouci.[7]
The site chosen for this summer retreat was in a secluded hollow.[8] It had originally been owned by the Marquess of Castelo Rodrigo. When the ruling Spanish were driven from Portugal in 1640, the property was confiscated, and Rodrigo was accused of having collaborated with the Spanish. The estate and its hunting lodge then became one of the many properties of the Portuguese king, João IV. He set it aside as one of the properties reserved for the second son of the reigning monarch.[9] Thus it came into the hands of Dom Pedro, the second son of João V.
The architect, Mateus Vicente de Oliveira, had trained under Ludovice of Ratisbon and Jean Baptiste Robillon[10] during the construction of the royal palace and convent of Mafra. The more sombre and massive classical palace at Mafra does not appear to have influenced the design for Queluz, which is in a lighter, more airy style.[1] Work began in 1747 and continued rapidly until 1755, when it was interrupted by the Great earthquake of 1755, after which the labourers were more urgently required for the reconstruction of the city. The earthquake proved to be a catalyst, because the urban rebuilding process stimulated the development of the arts in Portugal.[4] The subsequent architecture of Queluz was influenced by new ideas and concepts. When work recommenced in 1758, the design was adapted for fear of another earthquake. Thus the later works take the form of low, long buildings, more structurally stable than a single high block: as a result, viewed from a distance the palace resembles long enfilades linked by higher pavilions rather than one single construction.
+ Please note that some of our items will come with a tag stating "Return only accepted if tag is attached". There are no exceptions to this policy.
All my tiles are replicas made of polymer clay where the image actually becomes part of the clay through baking. No glue is used in the process. The pieces become waterproof and scratch resistant. Due to the handmade and hand shaped nature of each tile, slight variations will occur, as no two pieces are alike.
🌺ATTENTION: There is a 5% RESTOCKING fee per item PLUS a $3.50 fee for returned items.
🌸🌸🌸🌸🌸🌸🌸🌸🌸🌸🌸🌸🌸🌸🌸🌸🌸🌸
QUESTION: Are your tiles real antique Portuguese azulejo tiles?
ANSWER: Absolutely not. In our description of each item, we try to call attention to the theft and destruction of antique Portuguese tiles. Even the tiles found in flea markets and antique stores were most likely stolen off a building during the night. We have seen entire home facades disappear during the night to thieves. Thankfully, Portugal just passed a law declaring this theft a crime. We can only hope that it will one day be enforced.
For this reason, we have no part in this despicable crime. We make our own tiles from polymer clay. Ceramic would be far too heavy for earrings and impossible to mold into the shapes we want. For the hoops, we mold the clay as thin as we can get it, so that it will look pretty inside the hoops.
Share